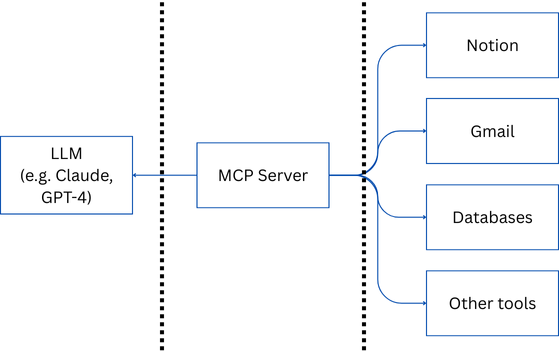
From Raw to Refined: The Data Medallion Architecture
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are swimming in a sea of information. But more data doesn’t always mean more insight. Often, it’s…
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are swimming in a sea of information. But more data doesn’t always mean more insight. Often, it’s a chaotic deluge, leaving teams struggling to find reliable, high-quality data for decision-making.

How do you tame this data beast and turn raw information into golden opportunities? This is where the Medallion Architecture design pattern can bring order to your data lakehouse.
Poor data quality can render even the most powerful tools useless, leading to inaccurate insights, inefficient processes, and ultimately, a failure to achieve business goals.
- Veda Bawo, a Director of Data Governance at Raymond James
In this article, we’ll dive into what Medallion Architecture is, explore its shiny benefits, look at a visual representation, and even discuss how you can demonstrate its principles with a simple example.
What is Medallion Architecture? 🏅
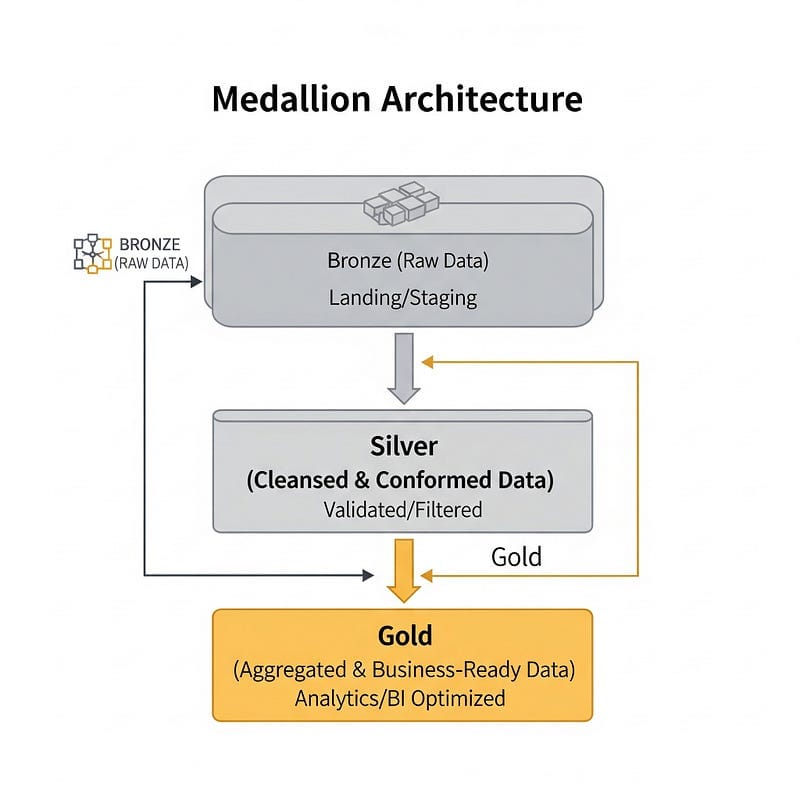
Medallion Architecture is a data design pattern that logically organises data. Think of it as a multi-stage filtration system, progressively refining your data as it moves through three distinct layers, which are Bronze, Silver, and Gold. The primary goal? To incrementally improve data quality, structure, and usability, ensuring that by the time data reaches your analysts and business users, it’s ready for action.
Here’s a visual to help you picture the flow:
Let’s break down these layers:
🥉 Bronze Layer (Raw Data / Landing/Staging):
- What it is: This is the first stop for all your source data. It lands here in its raw, untouched, and often messy format. Think of it as the “as-is” snapshot, preserving the original state.
- Data State: Raw, unfiltered, historical archive (e.g., JSON, CSV, Parquet from various sources).
- Purpose: Guarantees rapid data capture and provides a historical archive. It’s crucial for auditability and allows for reprocessing pipelines from scratch without needing to re-fetch from often ephemeral or rate-limited source systems. Schema variations are common here.
- Users: Primarily data engineers who manage the ingestion process.
🥈 Silver Layer (Cleansed & Conformed Data / Validated/Filtered):
- What it is: Data from the Bronze layer undergoes its first major transformation. Here, it’s cleaned, validated, de-duplicated, and conformed into a more structured and reliable format. This layer often provides an “enterprise view” of key business entities like customers, products, or transactions.
- Data State: Filtered, validated, enriched, joined, and standardized. Data models are applied, and data types are corrected.
- Purpose: To provide a reliable, queryable source for analytics, ad-hoc reporting, and as a dependable feed for data science projects. It’s more structured than Bronze but still somewhat granular.
- Users: Data engineers refining the data, data analysts performing exploratory analysis, and data scientists building foundational models.
🥇 Gold Layer (Aggregated & Business-Ready Data / Analytics/BI Optimised):
- What it is: This is the pinnacle of refinement. Data from the Silver layer is further transformed, aggregated, and organised into consumption-ready formats. These tables are typically project-specific and highly optimised for particular business intelligence, reporting, and advanced analytics use cases.
- Data State: Aggregated, business-level metrics, often denormalised or in star/snowflake schemas for optimal query performance.
- Purpose: Directly powers dashboards, BI reports, AI/ML applications, and allows business users to easily query data for specific insights without needing complex transformations.
- Users: Business analysts, BI developers, data scientists working on specific applications, and even executives consuming reports.
Why Bother? The Benefits of Going for Gold ✨
Implementing a Medallion Architecture might seem like extra work, but the payoff is significant:
- Improved Data Quality & Reliability: Each layer systematically cleanses and validates data, resulting in trustworthy insights from the Gold layer.
- Enhanced Data Governance & Lineage: The clear, staged approach makes it easier to track data transformations (data lineage) and apply governance rules.
- Scalability & Flexibility: The modular design allows different teams to work on different layers and makes it easier to update or add new data sources or transformations without breaking downstream processes.
- ACID Transactions & Time Travel (with Lakehouse Technologies): When implemented with technologies like Delta Lake, Apache Iceberg, or Apache Hudi, you get ACID transactions (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) for your data lake, ensuring reliability. Time travel allows you to access historical versions of your data, which is invaluable for debugging, audits, or rolling back changes.
- Simplified Data Debugging: If issues arise, you can isolate problems to specific layers, making debugging much more manageable than in a monolithic pipeline.
- Facilitates Self-Service Analytics & ML: The Gold layer provides clean, optimised, and ready-to-use data, empowering business users and data scientists.
- Cost Efficiency in the Long Run: While storing multiple copies of data has a cost, the optimised query performance on Silver and Gold tables, and the ability to rebuild from Bronze, can lead to overall processing cost savings and reduced development time.
Conclusion
The Medallion Architecture isn’t just a buzzword, it is a practical framework for building robust, reliable, and scalable data platforms. Refining data through Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers, organisations can ensure that their data is not just stored, but truly ready to drive insights and power decision-making.